👣 Ayak Sağlığının Önemi: Vücudun Temeli Ayaklardan Başlar
Gün boyunca bizi taşıyan ayaklarımız, aslında vücudumuzun en fazla yük alan yapısıdır. Ancak çoğu zaman onlara gereken özeni göstermeyiz. Oysa ayaklar, birçok ciddi hastalığın erken habercisi olabilir. Özellikle diyabet, kalp ve damar hastalıkları olan bireylerde düzenli ayak bakımı hayati önem taşır.
🦶 Podoloji Nedir?
Podoloji, ayak ve alt ekstremite sağlığıyla ilgilenen bilim dalıdır.
Podologlar, özel cihazlarla ayak yapısını 3 boyutlu olarak analiz eder ve gerekliyse kişiye özel ortopedik tabanlık tasarlayarak vücut dengesini ve yürüyüş konforunu düzeltir.
Yalnızca tabanlık yapmakla kalmazlar; hastaya doğru ayakkabı seçimi ve kullanım hakkında da rehberlik ederler.
⚙️ Ayak Problemleri ve Nedenleri
Yanlış ayakkabı seçimi, aşırı kilo, yanlış basış veya genetik faktörler; zamanla şu sorunlara yol açabilir:
-
Düz tabanlık (pes planus)
-
Yüksek taban (pes kavus)
-
Topuk dikeni (plantar fasiit)
-
Halluks valgus (başparmak çıkıntısı)
-
Morton nöroma (sinir sıkışması)
-
Diz, kalça ve bel ağrıları
-
Tırnak batması, nasır, siğil
Bu rahatsızlıkların çoğu, doğru analiz ve tabanlık desteğiyle kontrol altına alınabilir.
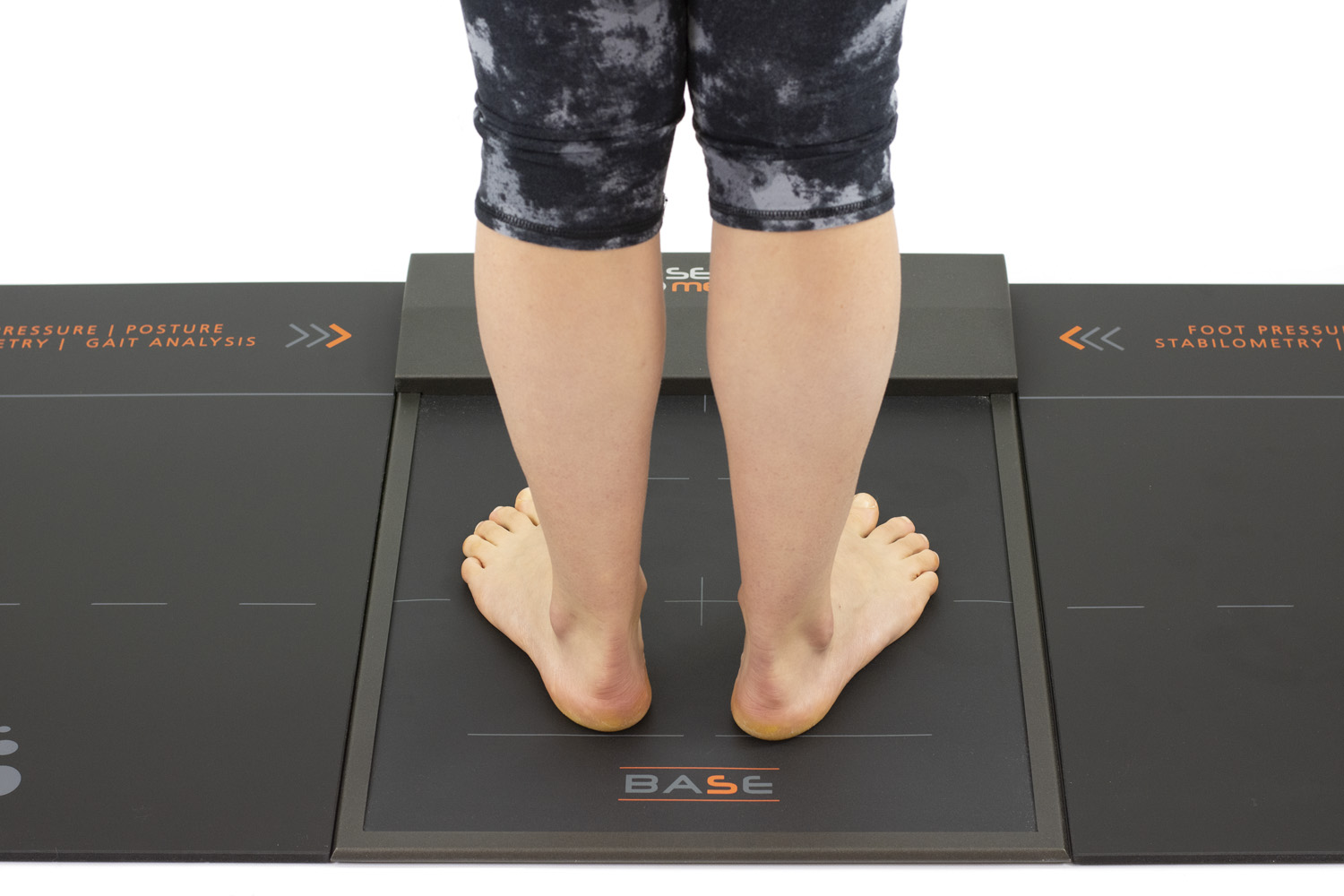
🧠 Baropodometrik Analiz: Ayak Basışınızı Görün
Gelişmiş sistemlerle yapılan baropodometrik analiz, ayak basınç haritasını çıkarır.
Kişi özel bir platformda yürür veya durur; bu sırada sensörler ayaktaki basınç dağılımını ölçer.
Sonuçlar, yürüyüş bozukluklarını ve dengesizlikleri tespit etmek için bilgisayar ortamında analiz edilir.
Bu veriler, kişiye özel tabanlık tasarımının temelini oluşturur.
👟 Kişiye Özel Tabanlık: Küçük Bir Adım, Büyük Bir Konfor
Kişiye özel tabanlıklar sadece bir rahatlık unsuru değil, tedavinin de en etkili tamamlayıcısıdır.
Düz taban, topuk dikeni veya ağrılı deformitelerde ayağın doğal yapısı desteklenir, yük dengesi sağlanır ve ağrılar azalır.
Ayrıca:
✅ Yorgunluğu azaltır
✅ Postürü (duruşu) düzeltir
✅ Sakatlık riskini düşürür
✅ Günlük yaşam ve spor performansını artırır
🌿 Sonuç: Sağlıklı Adımlar, Sağlıklı Yaşam
Ayaklar, vücudun dengesi ve hareket kabiliyetinin temelidir.
Onlara gösterilecek küçük bir özen, yaşam kalitenizi büyük ölçüde artırabilir.
Unutmayın: Sağlıklı bir yaşamın ilk adımı, doğru basmaktan geçer.